How do I perform a similarity search?
Last updated on November 18, 2025
A similarity search can be used to find substances or reactions that are similar, but do not meet all criteria of the query structure:
- A compound/structure is said to be similar if the new structure's behavior or ”look” is close to the starting structure.
- A reaction is said to be similar if the reaction center of the transition state remains unchanged but certain parts of the structures of the starting materials and products may be replaced or extended.
The chemical structures in Reaxys are processed to analyze them for cyclic and acyclic features. Based on the result of this analysis, fingerprints for the chains and the rings of a given structure are generated and concatenated to finally form a classification string as representation of the given structure. All structures of the entire Reaxys database have been processed this way resulting in a continuum of fingerprints, which then has been subdivided into clusters of similar fingerprints according to certain ring and chain characteristics.
By entering a structure query (without substructure or R-group query attributes) and selecting the similarity search feature, Reaxys will analyze the given query structure and create various search strings.
How
You can perform a similarity search on substances, reactions, or products. Click the topic of your interest to see the steps.
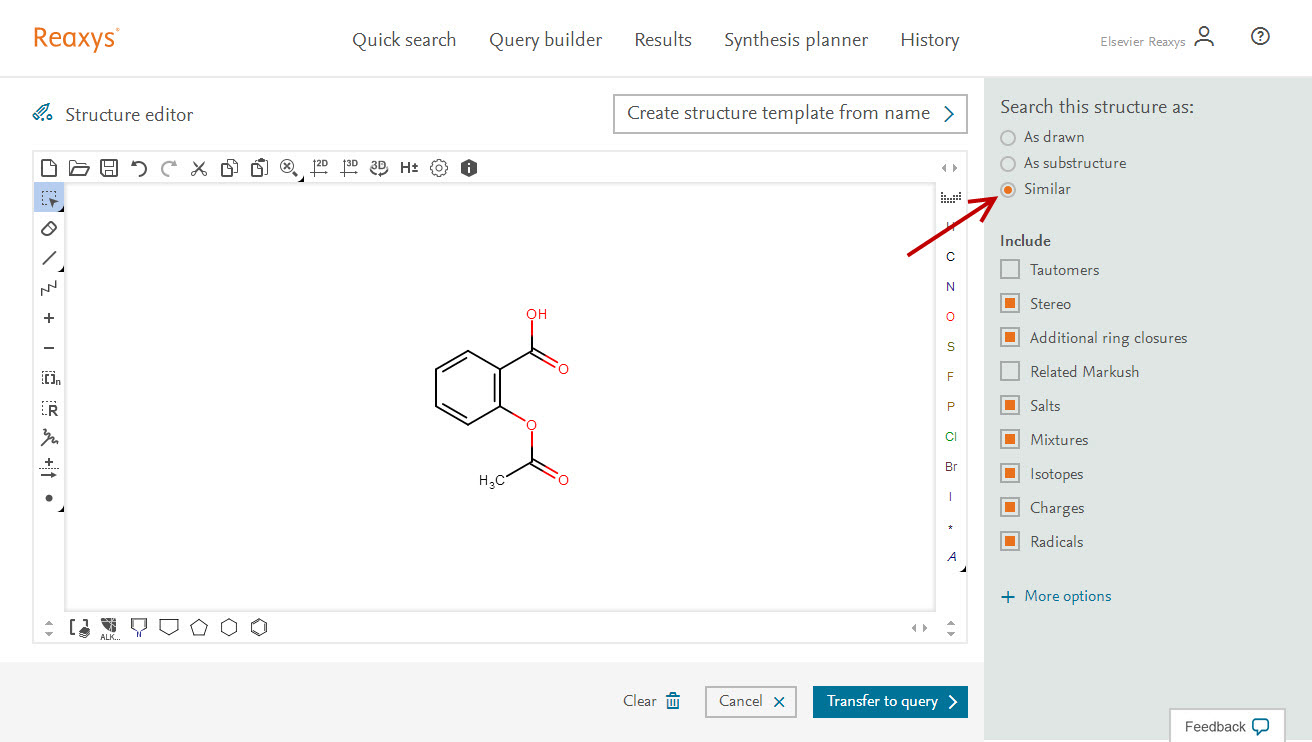
Follow these steps to perform a similarity search for Substances:
- Either:
Open the Quick search tab and click ‘Create Structure or Reaction drawing’
OR
- Open the Query builder tab, click ‘Structure’ in the top toolbar and then click ‘Create Structure or Reaction drawing’ to open the Structure editor.
- Click ‘Transfer to query’.
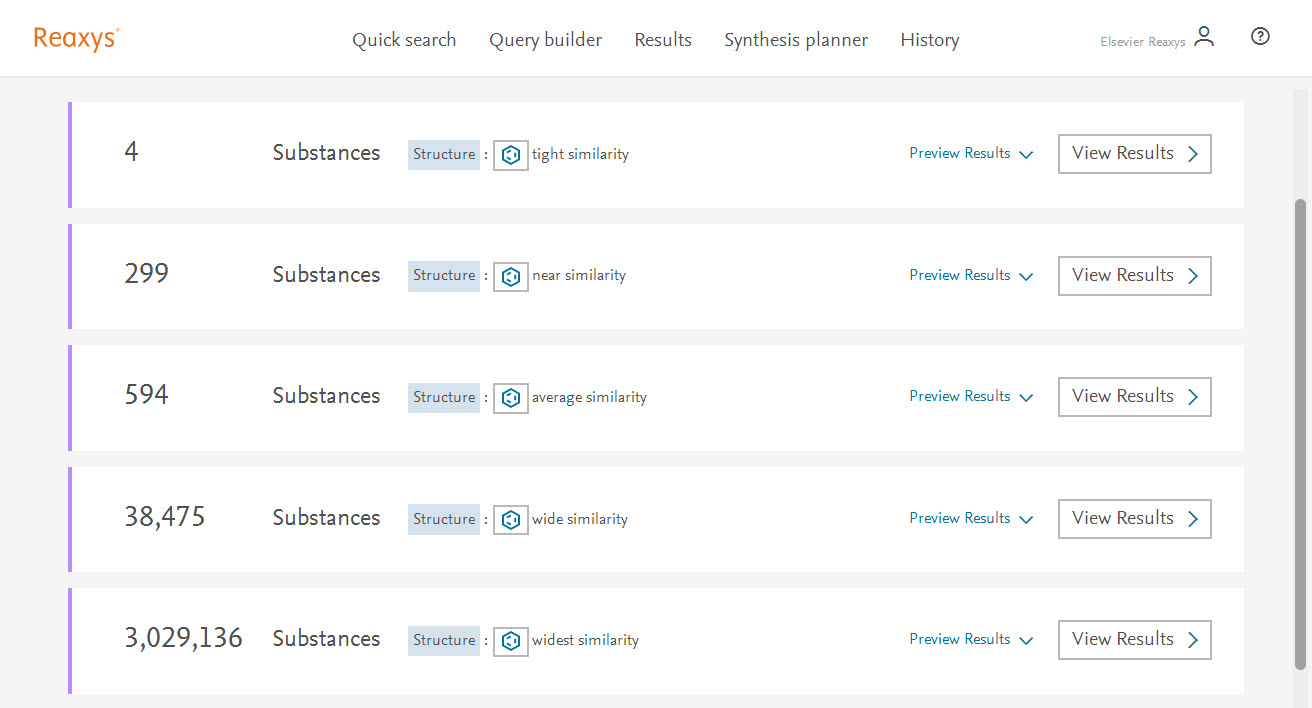
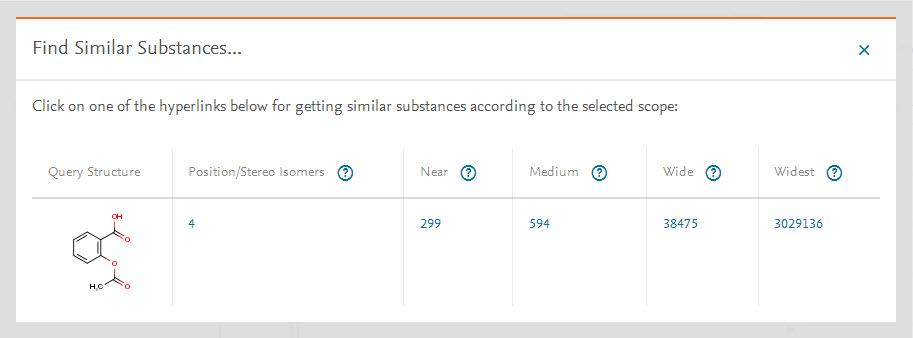
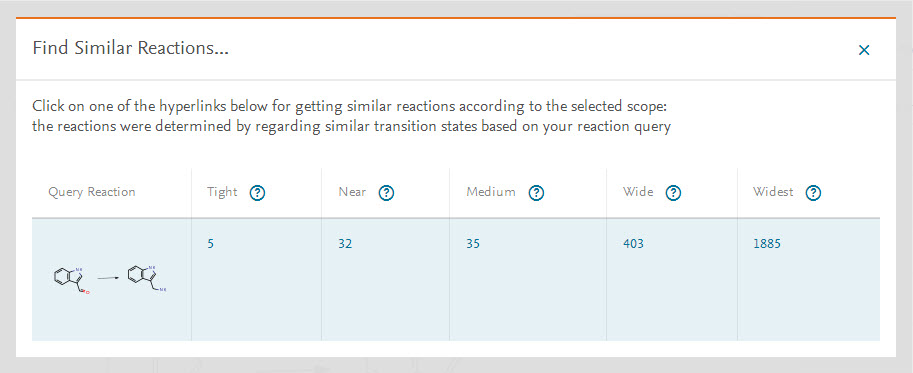
The results will give you up to 5 options to choose from, with varying degrees of similarity:
- Tight (Positional/stereo isomers) - Isomeric structures with different arrangements of the given structural elements (roughly equivalent to 95% similarity).
- Near- Includes structures containing the same ring and chain systems (possibly multiple) with the original relative positions of substituents and extended by further simple substituents such as hydrocarbons (roughly equivalent to 80% similarity).
- Medium/Average- Includes structures with a wider range of rings and substituents: the degree of unsaturation, form, and substitution pattern of rings is extended (roughly equivalent to 60% similarity).
- Wide- Includes a still wider range of substituents but retaining, to some extent, the influence of the relative positions of substituents (roughly equivalent to 40% similarity).
- Widest- Same as Wide, but without any restrictions on the relative positions of substituents (roughly equivalent to 20% similarity).
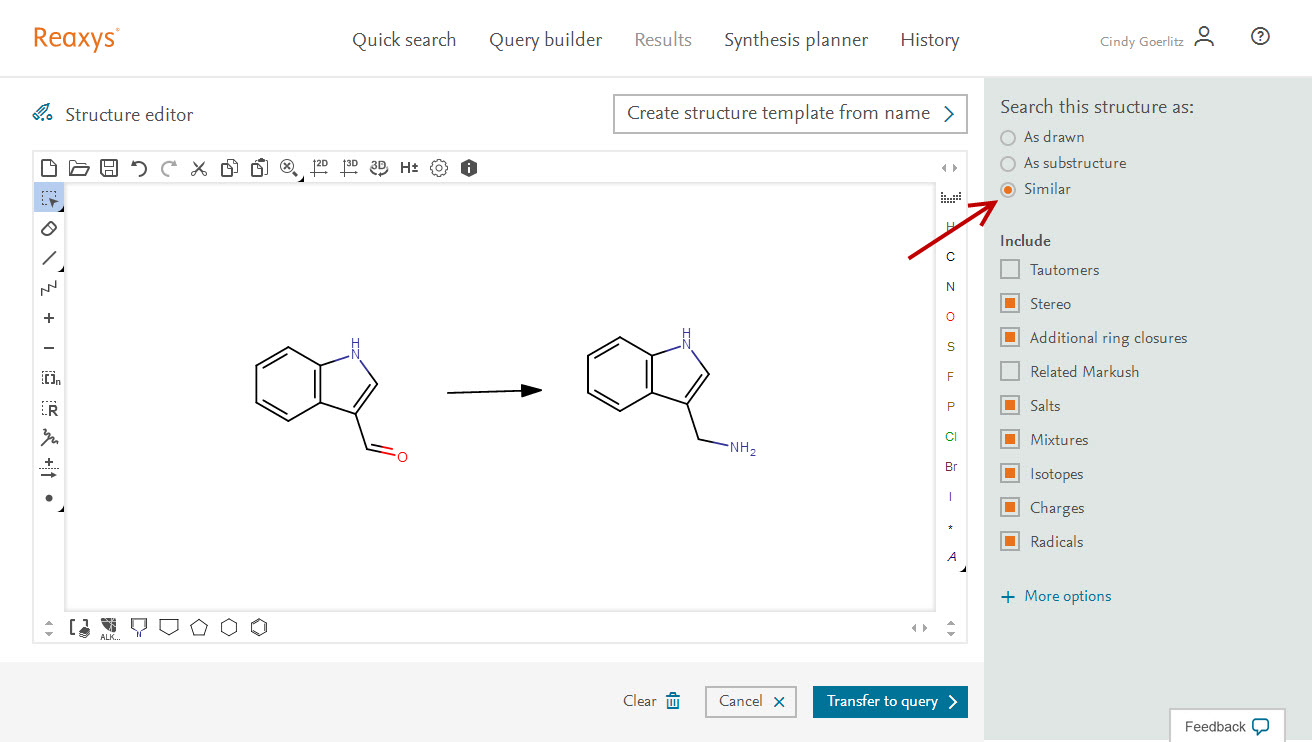
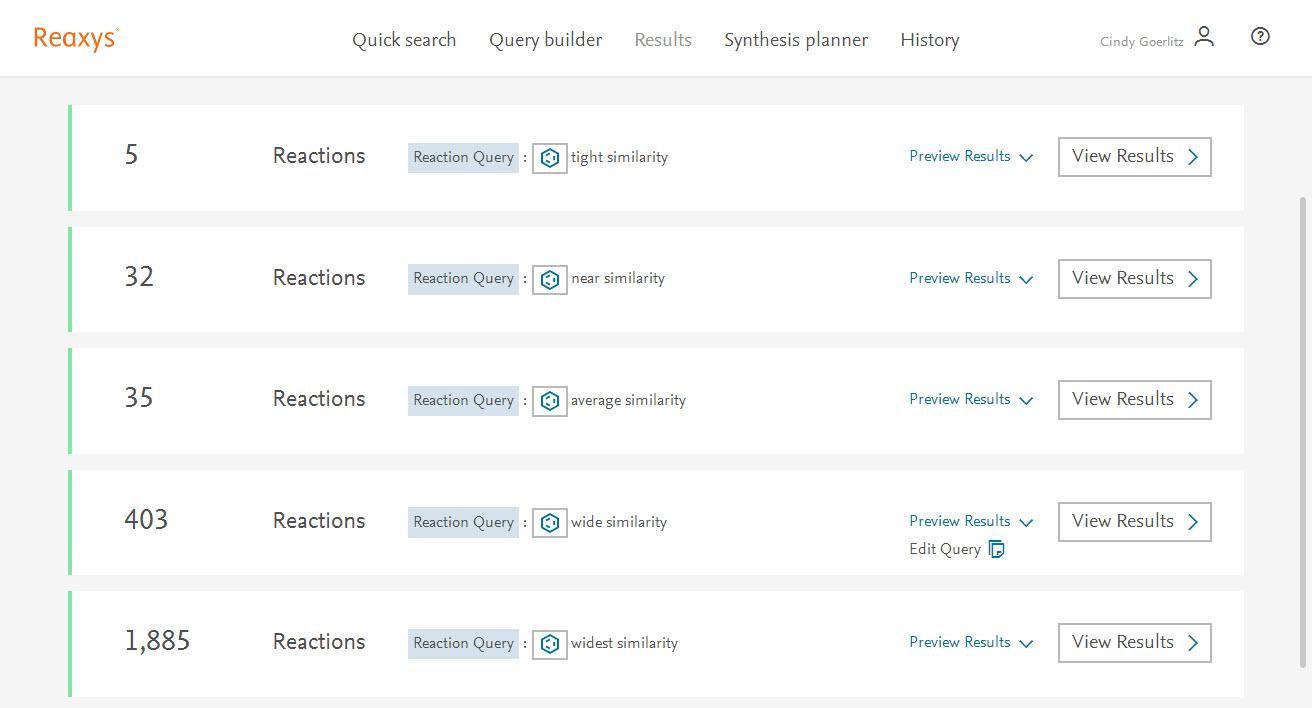
Follow these steps to perform a similarity search for Reactions:
- Either:
Open the Quick search tab and click ‘Create Structure or Reaction drawing’
OR
- Open the Query builder tab, click ‘Structure’ in the top toolbar and then click ‘Create Structure or Reaction drawing’ to open the Structure editor.
- Click ‘Transfer to query’.
The results will give you up to 5 options to choose from, with varying degrees of similarity:
- Tight – Similar reactions on the basis of the atom spheres 1 to 5 of the starting material/product relationship(s), i.e. the overlap of atoms and bonds alpha and beta to the reaction center.
- Near - Similar reactions on the basis of the atom spheres 1 to 4 of the starting material/product relationship(s), i.e. the overlap of atoms alpha and beta to the reaction center.
- Medium/Average - Similar reactions on the basis of the atom spheres 1 to 3 of the starting material/product relationship(s), i.e. the overlap of atoms and bonds alpha to the reaction center.
- Wide - Similar reactions on the basis of the atom spheres 1 to 2 of the starting material/product relationship(s), i.e. the overlap of atoms alpha to the reaction center.
- Widest - Similar reactions on the basis of the direct atom sphere of the starting material/product relationship(s), i.e. the overlap of atoms of the reaction center.
Please note: Results do not include isotopes, mixtures, salts, additional rings or tautomers. A halogen in the query may be replaced by a different halogen in the results. Explicit hydrogens are ignored in the search. Atom mapping is ignored during the search.
The degree of similarity between any two given reactions is determined by:
- The nature of the transformations involved (reaction centers).
- The nature of the unchanged atoms immediately surrounding these centers.
A greater amount of weight is placed on the reaction centers in the starting materials and the atoms immediately attached to them.
Atoms involved in a Reaction Centre (RC) are the set of those atoms that involve bond changes as the starting material converts to the product. Bonds may be made or broken, and/or the formal bond order may change. The RC description is then this set of atoms, with explicit connections to each of its attached partners in the RC set.
When you perform a Reaction Similarity search using just one structure (with or without the arrow) Reaxys will consider "structure similarity" just as it would if you were searching for a single substance.
Did we answer your question?
Related answers
Recently viewed answers
Functionality disabled due to your cookie preferences