How do I define Reaxys Generic Groups?
Last updated on October 16, 2025
The Reaxys Group Generics tool is used to define acyclic groups and cyclic groups, while the Query Atoms tool is used to define atom generics.
These predefined generic groups are recognized by Reaxys regardless of the structure editor that created the query.
How
Click on one of the topics below to learn more about the specific generic groups and how to define them:
Follow these steps to define your generic groups:
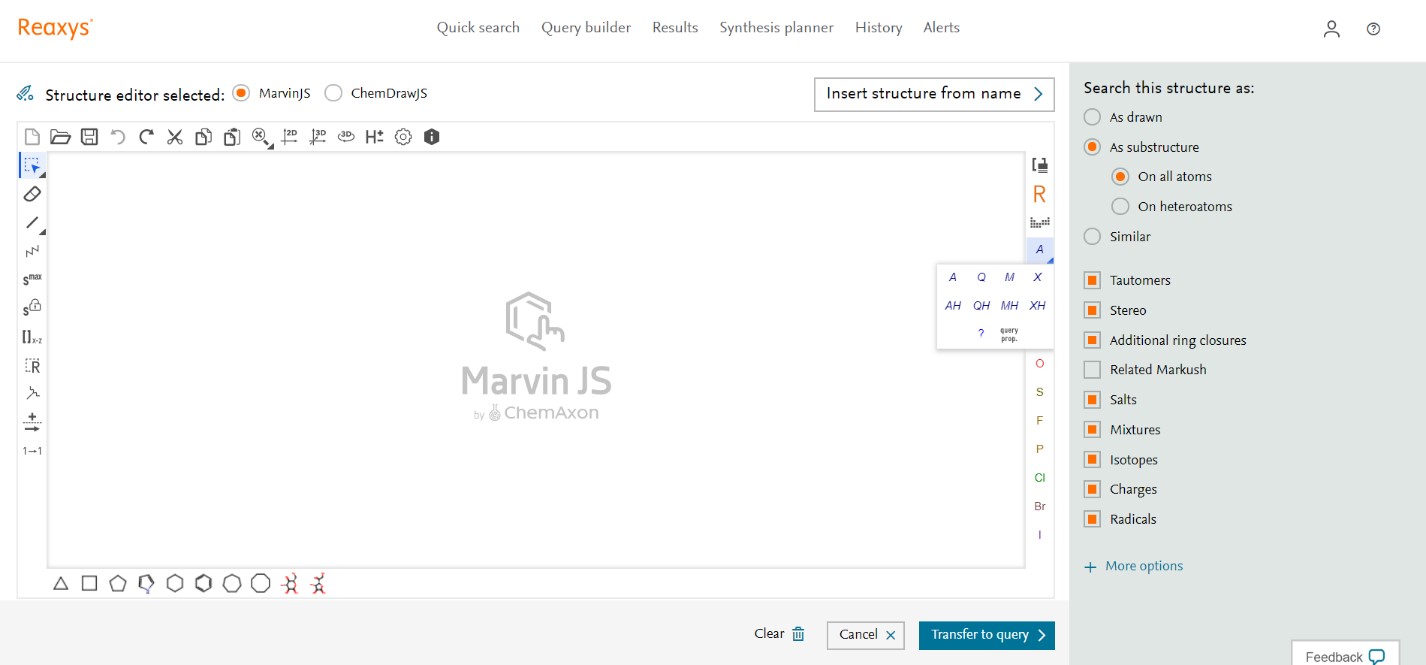
- Click ‘Create Structure or Reaction Drawing’ on the Reaxys home page to open the Marvin JS Structure editor.
- Click the R… tool on the left side of the bottom Template Toolbar.
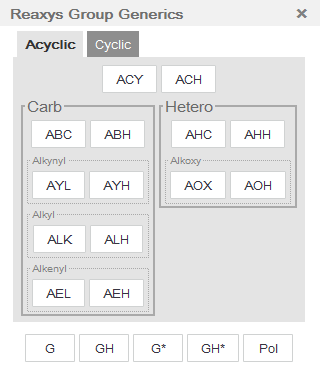
- In the popup window choose the desired generic group from a predefined list of group generics.
- The groups are arranged with the most generic groups at the top of the window, and the least generic at the bottom.
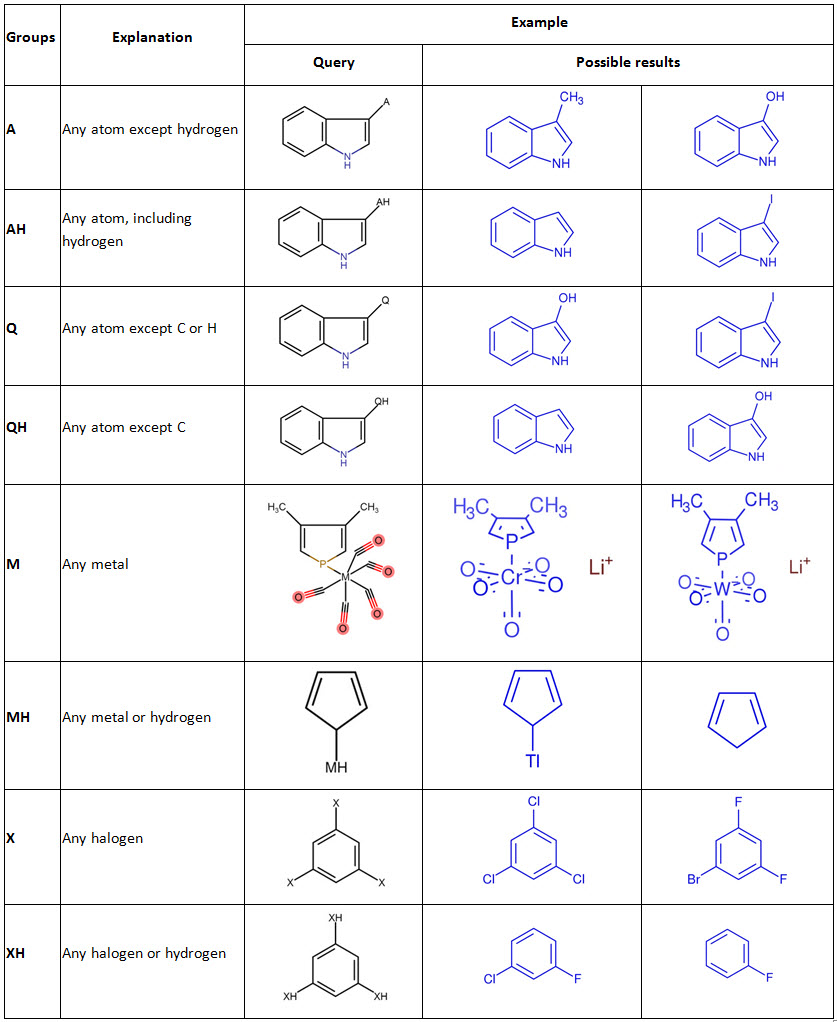
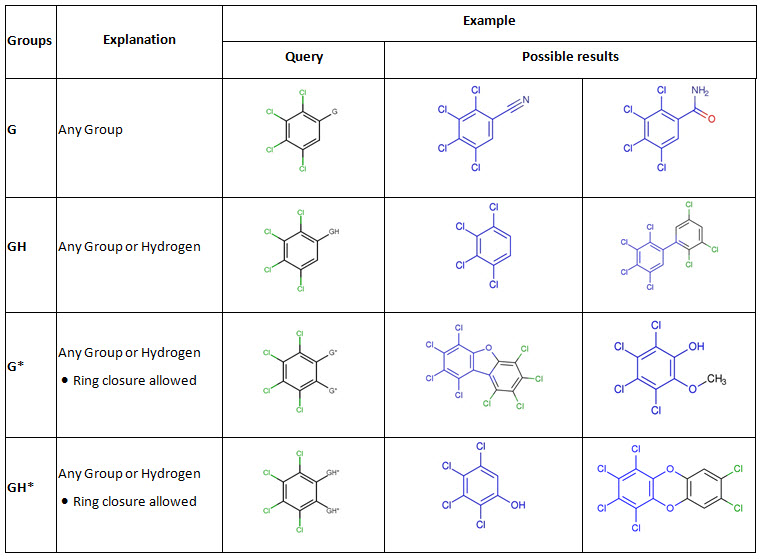
- Learn more about Generic Groups G and GH
The Generic Groups G and GH will retrieve any group (G) and any group or hydrogen (GH).
Group names that are marked with an asterisk (G*, GH*) retrieve the same as G and GH, but they also retrieve structures in which an atom in the group can be linked with an atom in the original structure to form a ring (ring closure). G and GH will not allow such implicit ring closures.
G and G* are unique among the Reaxys Generics because they will accept more than 1 attachment point.
Please note: the Reaxys Query Form setting "No additional rings" must not be checked if you want to allow G* or GH* to form a ring with the rest of the structure. It is recommended that you perform a substructure search if you want to retrieve substances with this type of ring closure.
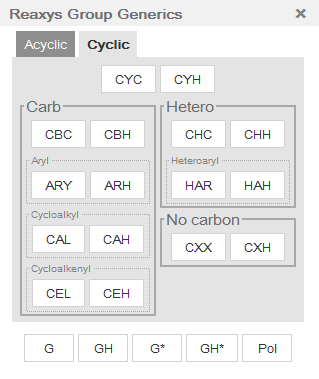
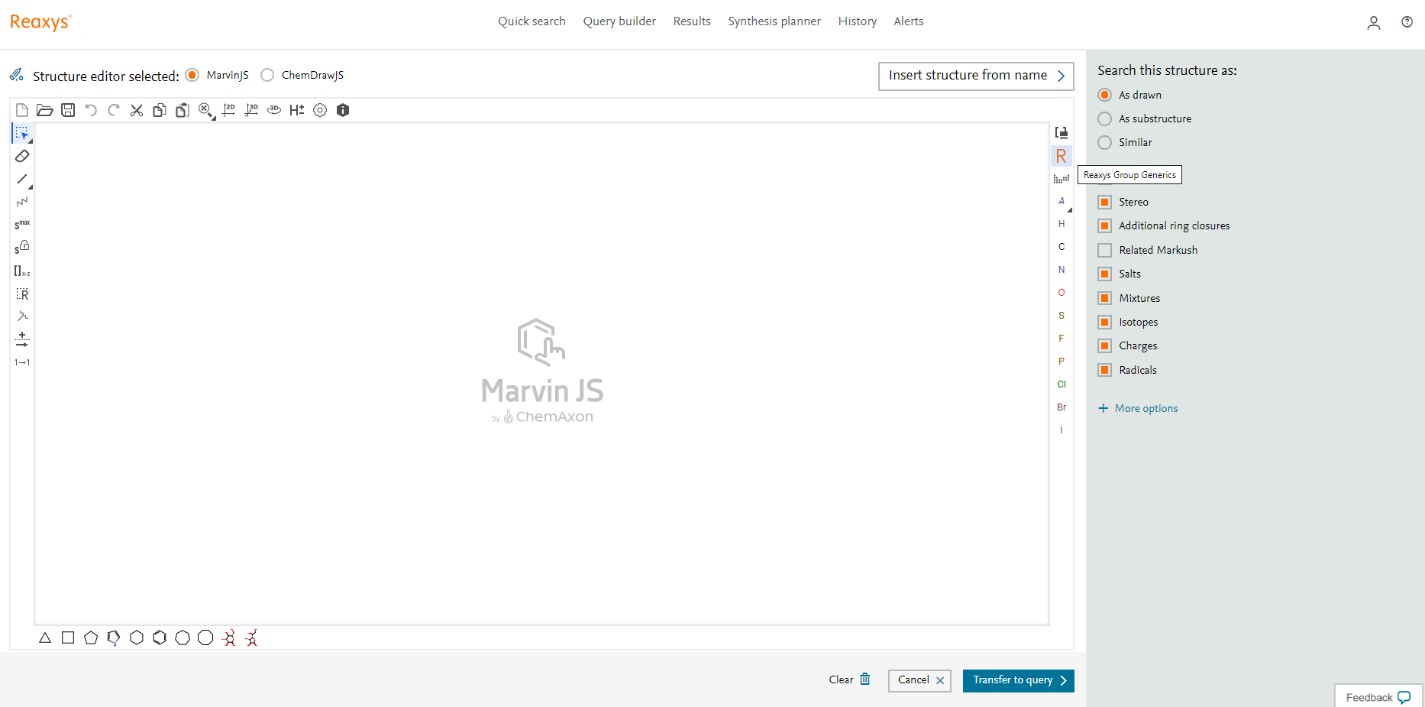
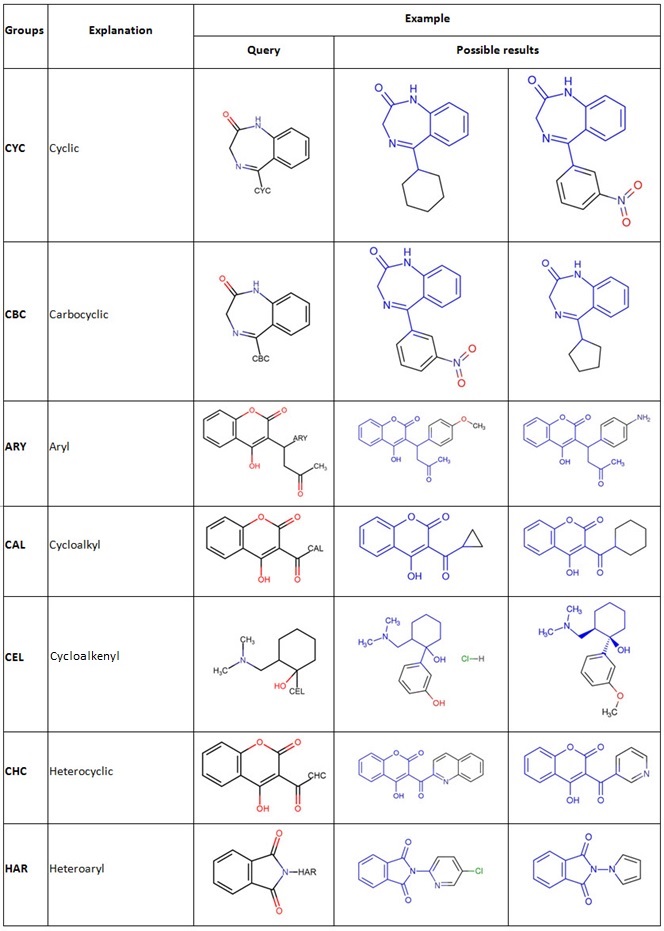
- Learn more about Cyclic Generic Groups
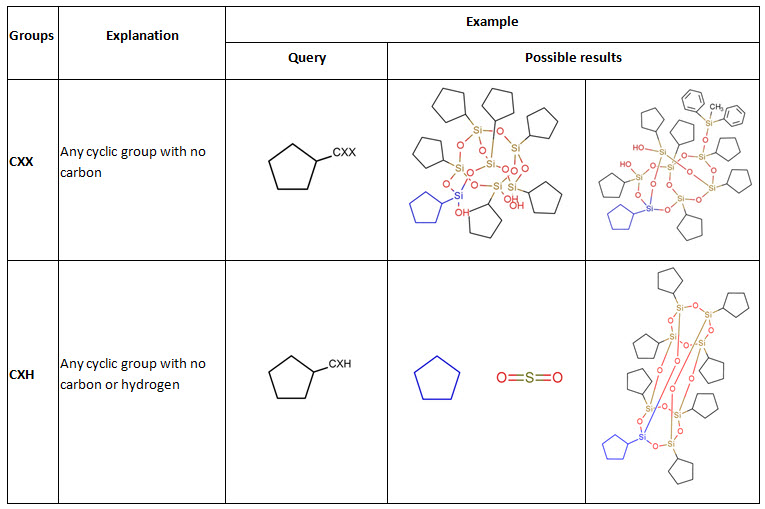
Group names that end in H allow either the group or hydrogen at that position. For example, CYC represents a cyclic group, while CYH represents a cyclic group or hydrogen.
Please note:
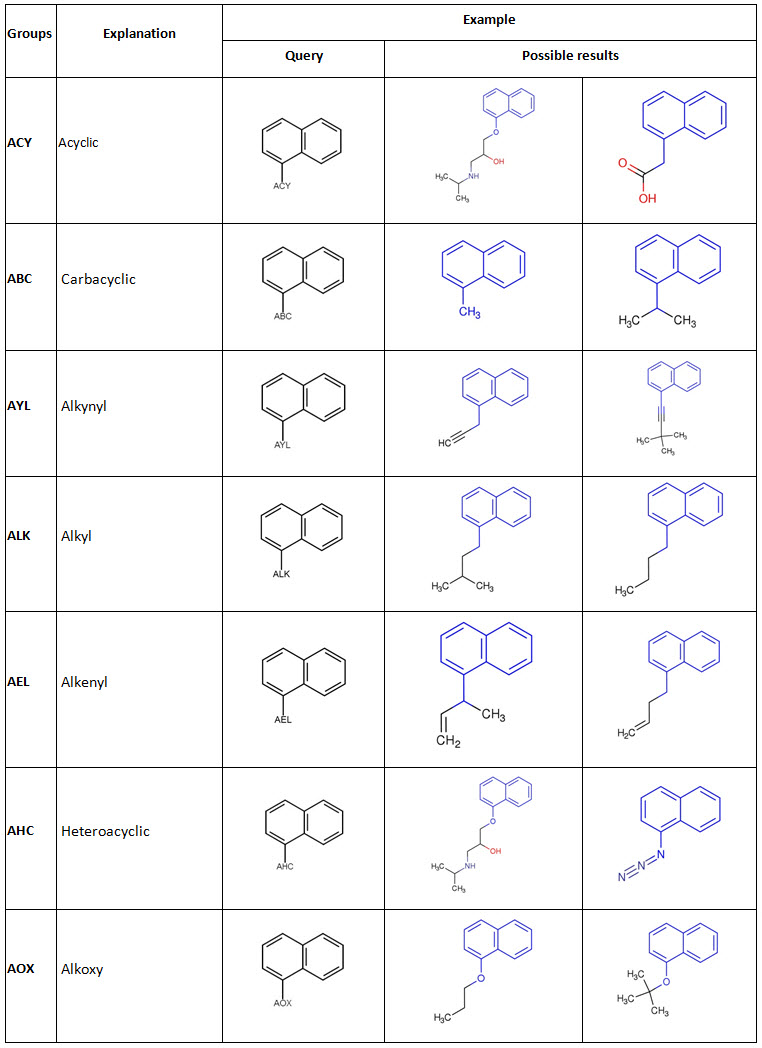
- an "ARY" group (aryl) is defined as a structure of n (n>0) optionally fused benzene rings and their respective substituted systems. The Aryl system must be directly attached to the parent.
- an "HAR" group (heteroaryl) is defined as a structure of n (n>0) optionally fused heteroaromatic rings and their respective substituted systems. A heteroaromatic ring is defined as five-, six- or seven-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds. At least one of the heteroaromatic rings must contain one or more hetero-atoms. The Heteroaryl system must be directly attached to the parent.
- After clicking the appropriate button, the dialog automatically closes, and the generic group will appear on the tip of the mouse cursor.
Did we answer your question?
Related answers
Recently viewed answers
Functionality disabled due to your cookie preferences